Abstract
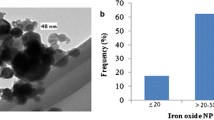
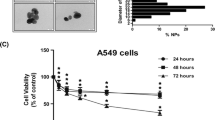
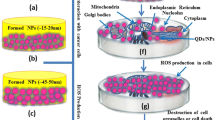
Concerns about the risk of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) to human health and environment are gradually increasing due to their wide range of applications. In this study, cytotoxicity, DNA damage, and apoptosis induced by TiO2 NPs (5 nm) in A549 cells were investigated. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays revealed the time- and concentration-dependent cytotoxic effects of TiO2 NPs in a concentration range of 50 to 200 μg/mL. A statistically significant (p < 0.05) induction in DNA damage was observed by the comet assay in cells exposed to 50 to 200 μg/mL TiO2 NPs for 48 h. A significant (p < 0.05) induction in micronucleus formation determined by 4,6-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining was also observed at the above concentrations. Typical apoptotic morphological feature and apoptotic bodies in A549 cells induced by TiO2 NPs at the above concentrations were observed by scanning electron micrographs. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that the cells treated with TiO2 NPs at concentrations of 100 and 200 μg/mL showed a significant G2/M phase arrest and a significant increased proportion of apoptotic cells. TiO2 NPs also disrupted the mitochondrial membrane potential evaluated by rhodamine 123 staining. Further analysis by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) indicated that the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-9 messenger RNA (mRNA) was increased significantly at the concentrations of 100 and 200 μg/mL TiO2 NPs for 48 h. Taken together, these findings suggest that TiO2 NPs can inhibit A549 cell proliferation, cause DNA damage, and induce apoptosis via a mechanism primarily involving the activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. The assay data provide strong evidence that TiO2 NPs can induce cytotoxicity, significant DNA damage, and apoptosis of A549 cells, suggesting that exposure to TiO2 NPs could cause cell injury and be hazardous to health.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrie C, Bachelet M, Vayssier-Taussat M, Russo-Marie F, Bouchaert I, Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon JM, Pinsky MR, Dhainaut JF, Polla BS (2001) Mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptosis peripheral blood monocytes in severe human sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164(3):389–395
Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WC (2012) The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 14:1–16
Andersson PO, Lejon C, Ekstrand-Hammarstrom B, Akfur C, Ahlinder L, Bucht A, Osterlund L (2011) Polymorph- and size-dependent uptake and toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles in living lung epithelial cells. Small 7(4):514–523
Aueviriyavit S, Phummiratch D, Kulthong K, Maniratanachote R (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles-mediated in vitro cytotoxicity does not induce hsp70 and grp78 expression in human bronchial epithelial A549 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 149:123–132. doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9403-z
Autrup H, Foldberg R, Deng F, Dang DA, Olesen P (2009) Ag and TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative stress in A549 cells. Toxicol Let 189(SI):S181–S181. doi:10.1016/j. toxlet. 2009.06.633
Bauer S, Park J, Faltenbacher J, Berger S, von der Mark K, Schmuki P (2009) Size selective behavior of mesenchymal stem cells on ZrO2 and TiO2 nanotube arrays. Integr Biol 1:525–532
Bermudez E, Mangum JB, Wong BA, Asgharian B, Hext PM, Warheit DB, Everitt JI (2004) Pulmonary responses of mice, rats, and hamsters to subchronic inhalation of ultrafine titanium dioxide particles. Toxicol Sci 77:347–357
Bernardeschi M, Guidi P, Scarcelli V, Frenzilli G, Nigro M (2010) Genotoxic potential of TiO2 on bottle nose dolphin leukocytes. Anal Bioanal Chem 396(2):619–623
Bhattacharya K, Davoren M, Boertz J, Schins RP, Hoffmann E, Dopp E (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:17
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107(7):2891–2959
Chen HW, Su SF, Chien CT, Lin WH, Yu SL, Chou CC, Chen JJ, Yang PC (2006) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce emphysema-like lung injury in mice. FASEB J 20(13):2393–2395
Choi HS, Ashitate Y, Lee JH, Kim SH, Matsui A, Insin N, Bawendi MG, Semmler-Behnke M, Frangioni JV, Tsuda A (2010) Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat Biotechnol 28:1300–1303
Cui Y, Gong X, Duan Y, Li N, Hu R, Liu H, Hong M, Zhou M, Wang L, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Hepatocyte apoptosis and its molecular mechanisms in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):874–880. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2010.07.109
Cui HY, Wang CL, Wang YR, Li ZJ, Zhang YN, Chen MH, Li FJ (2014) Pleurotus nebrodensis polysaccharide induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Carbohyd Polym. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.001
Falck GC, Lindberg HK, Suhonen S, Vippola M, Vanhala E, Catalan J, Savolainen K, Norppa H (2009) Genotoxic effects of nanosized and fine TiO2. Hum Exp Toxicol 28(6–7):339–352. doi:10.1177/0960327109105163
Ferin J, Oberdörster G, Penney DP (1992) Pulmonary retention of ultrafine and fine particles in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6:535–542
Freyre-Fonsecaa V, Delgado-Buenrostroa NL, Gutiérrez-Cirlosb EB, Calderón-Torresa CM, Cabellos-Avelarb T, Sánchez-Pérezc Y, Pinzónd E, Torresd I, Molina-Jijóne E, Zazuetaf C, Pedraza-Chaverrie J, García-Cuéllarc CM, Yolanda I, Chirino YI (2011) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles impair lung mitochondrial function. Toxicol Lett 202(2):111–119. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.01.025
Gao G, Ze Y, Li B, Zhao X, Zhang T, Sheng L, Hu R, Gui S, Sang X, Sun Q, Cheng J, Cheng Z, Wang L, Tang M, Hong F (2012) Ovarian dysfunction and gene-expressed characteristics of female mice caused by long-term exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J HAZARD MATER 243:19–27
Gao A, Hang R, Huang X, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang L, Tang B, Ma S, Chu PK (2014) The effects of titania nanotubes with embedded silver oxide nanoparticles on bacteria and osteoblasts. Biomaterials. Pii, S0142-9612 (14) 00088-X. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014. 01.058
Gheshlaghi ZN, Riazi GH, Ahmadian S, Ghafari M, Mahinpour R (2008) Toxicity and interaction of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with microtubule protein. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 40(9):777–782
Ghosh M, Bandyopadhyay M, Mukherjee A (2010) Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles at two trophic levels: plant and human lymphocytes. Chemosphere 81(10):1253–1262. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.022
Gui SX, Zhang ZL, Zheng L, Cui YL, Liu XR, Li N, Hong FS (2011) Molecular mechanism of kidney injury of mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 195:365–370
Gurr JR, Wang ASS, Chen CH, Jan KY (2005) Ultrafine titanium dioxide particles in the absence of photoactivation can induce oxidative damage to human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicology 213(1–2):66–73
Heemels MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407(6805):770–776. doi:10.1038/ 35037710
Heinrich U, Fuhst R, Rittinghausen S, Creutzenberg O, Bellman B, Koch W, Levsen K (1995) Chronic inhalation exposure of Wistar rats and two different strains of mice to diesel engine exhaust, carbon black, and titanium dioxide. Inhal Toxicol 7:533–556
Hoet PH, Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Salata OV (2004) Nanoparticles—known and unknown health risks. J Nanobiotechnol 2:12. doi:10.1186/1477-3155-2-12
Hsiao IL, Huang YJ (2011) Improving the interferences of methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium and IL-8 assays in assessing the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(6):5228–5233. doi:10.1166/jnn.2011.4132
Husain M, Saber AT, Guo C, Jacobsen NR, Jensen KA, Yauk CL, Williams A, Vogel U, Wallin H, Halappanavar S (2013) Pulmonary instillation of low doses of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mice leads to particle retention and gene expression changes in the absence of inflammation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 269(3):250–62. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.03.018
Hussain S, Thomassen LC, Ferecatu I, Borot MC, Andreau K, Martens JA, Fleury J, Baeza-Squiban A, Marano F, Boland S (2010) Carbon black and titanium dioxide nanoparticles elicit distinct apoptotic pathways in bronchial epithelial cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:10
IRAC (2006) IARC: cobalt in hard metals and cobalt sulfate, gallium arsenide, indium phosphide and vanadium pentoxide. IARC. Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 86
Jeon YM, Park SK, Kim WJ, Ham JH, Lee MY (2011) The effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on the protein expression in mouse lung. Mol Cell Toxicol 7:283–289. doi:10.1007/s13273-011-0034-9
Jin CY, Zhu BS, Wang XF, Lu QH (2008) Cytotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mouse fibroblast cells. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1871–1877. doi:10.1021/tx800179f
Kang SJ, Kim BM, Lee YJ, Chung HW (2008) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles trigger P53-mediated damage response in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 49(5):399–405. doi:10.1002/em.20399
Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L, Van Ravenzwaay B, Schulz M, Wiench K, Champ S, Schulte S, Wohlleben W, Oesch F (2010) Gene toxicity studies on titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanomaterials used for UV-protection in cosmetic formulations. Nanotoxicology 4:364–381
Lee YS, Yoon S, Yoon HJ, Lee K, Yoon HK, Lee JH, Song CW (2009) Inhibitor of differentiation 1 (Id1) expression attenuates the degree of TiO2-induced cytotoxicity in H1299 non-small cell lung cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 189:191–199
Li N, Duan Y, Hong M, Zheng L, Fei M, Zhao X, Wang J, Cui Y, Liu H, Cai J, Gong S, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Spleen injury and apoptotic pathway in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticules. Toxicol Lett 195(2–3):161–168
Limbach LK, Li YC, Grass RN, Brunner TJ, Hintermann MA, Muller M, Gunther D, Stark WJ (2005) Oxide nanoparticle uptake in human lung fibroblasts: effects of particle size, agglomeration, and diffusion at low concentrations. Environ Sci Tech 39:9370–376
Lindberg HK, Falck GC, Catalán J, Koivisto AJ, Suhonen S, Järventaus H, Rossi EM, Nykäsenoja H, Peltonen Y, Moreno C, Alenius H, Tuomi T, Savolainen KM, Norppa H (2012) Genotoxicity of inhaled nanosized TiO2 in mice. Mutat Res 745(1–2):58–64
Liu HT, Ma LL, Zhao JF, Liu J, Yan JY, Ruan J, Hong FS (2009) Biochemical toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 particles in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 129:170–180
Liu SC, Xu LJ, Zhang T, Ren GG, Yang Z (2010) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by nanosized titanium dioxide in PC12 cells. Toxicol 267(1–3):172–177. doi:10.1016/j.tox 2009.11.012
Lowe SW, Lin AW (2000) Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 21:485–95
McLeish IA, Bell S, McKay T, Tenev T, Marani M, Lemoine NR (2003) Expression of Smac/DIABLO in ovarian carcinoma cells induces apoptosis via a caspase-9-mediated pathway. Exp Cell Res 286(2):186–198
Meena R, Paulraj R (2012) Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of TiO2 nano anatase in liver and kidney of Wistar rat. Toxico Enviro Chem 94(1):146–163. doi:10.1080/02772248. 2011. 638441
Meng H, Xia T, George S, Nel AE (2009) A predictive toxicological paradigm for the safety assessment of nanomaterials. ACS Nano 3(7):1620–1677. doi:10.1021/nn9005973
Mondal D, Nguyen L, Oh IH, Lee BT (2013) Microstructure and biocompatibility of composite biomaterials fabricated from titanium and tricalcium phosphate by spark plasma sintering. J, Biomed, Mater, Res, A 101(5):1489–1501. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34455
Monteiller C, Tran L, MacNee W, Faux S, Jones A, Miller B, Donaldson K (2007) The pro-inflammatory effects of low-toxicity low-solubility particles, nanoparticles and fine particles, on epithelial cells in vitro: the role of surface area. Occup Environ Med 64(9):609–615. doi:10.1136/oem.2005.024802
Naya M, Kobayashi N, Ema M, Kasamoto S, Fukumuro M, Takami S, Nakajima M, Hayashi M, Nakanishi J (2012) In vivo genotoxicity study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using comet assay following intratracheal instillation in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 62:1–6
Noël A, Charbonneau M, Cloutier Y, Tardif R, Truchon G (2013) Rat pulmonary responses to inhaled nano-TiO2: effect of primary particle size and agglomeration state. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:48. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-10-48
Oberdörster G, Ferin J, Lehnert BE (1994) Correlation between particle size, in vivo particle persistence, and lung injury. Environ Health Perspect 102:173–179
Oberdörster G, Finkelstein JN, Johnston C, Gelein R, Cox C, Baggs R, Elder AC (2000) Acute pulmonary effects of ultrafine particles in rats and mice. Res Rep Health Eff Inst 96:5–74, disc. 75–86
Oberdörster G, Sharp Z, Atudorei V, Elder A, Gelein R, Kreyling W, Cox C (2004) Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal Toxicol 6:437–445
Park J, Bauer S, von der Mark K, Schmuki P (2007a) Nanosize and vitality: TiO2 nanotube diameter directs cell fate. Nano Lett 7:1686–1691
Park S, Lee YK, Jung M, Kim KH, Chung N, Ahn EK, Lim Y, Lee KH (2007b) Cellular toxicity of various inhalable metal nanoparticles on human alveolar epithelial cells. Inhal Toxicol 19(1):59–65. doi:10.1080/08958370701493282
Park EJ, Yi J, Chung KH, Ryu DY, Choi J, Park K (2008) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett 180:222–229
Park J, Bauer S, Schlegel KA, Neukam FW, von der Mark K, Schmuki P (2009) TiO2 nanotube surfaces: 15 nm—an optimal length scale of surface topography for cell adhesion and differentiation. Small 5:666–671
Park EJ, Shim HW, Lee GH, Kim JH, Kim DW (2013) Comparison of toxicity between the different-type TiO2 nanowires in vivo and in vitro. Arch Toxicol 87:1219–1230. doi:10.1007/s00204-013-1019-3
Petkovic J, Zegura B, Stevanovic M, Drnovsek N, Uskokovic D, Novak S, Filipic M (2011) DNA damage and alterations in expression of DNA damage responsive genes induced by TiO2 nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Nanotoxicology 5(3):341–353. doi:10.3109/17435390.2010.507316
Porter AG, Janicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6(2):99–104
Porter DW, Wu N, Hubbs A, Mercer R, Funk K, Meng F, Li J, Wolfarth M, Battelli L, Friend S, Andrew M, Hamilton R, Sriram K, Yang F, Castranova V, Holian A (2013) Differential mouse pulmonary dose- and time course-responses to titanium dioxide nanospheres and nanobelts. Toxicol Sci 131:179–193
Ramkumar KM, Manjula C, GnanaKumar G, Kanjwal MA, Sekar TV, Paulmurugan R, Rajaguru P (2012) Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction by TiO2 nanofibers in HeLa cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 81(2):324–333. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb. 2012.02.013
Reeves JF, Davies SJ, Dodd NJF, Jha AN (2008) Hydroxyl radicals (OH) are associated with titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative DNA damage in fish cells. Mutat Res 640(1–2):113–122. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.12.010
Renwick LC, Brown D, Clouter A, Donaldson K (2004) Increased inflammation and altered macrophage chemotactic responses caused by two ultrafine particle types. Occup Environ Med 61(5):442–447
Rivera-Chacon DM, Alvarado-Velez M, Acevedo-Morantes CY, Singh SP, Gultepe E, Nagesha D, Sridhar S, Ramirez-Vick JE (2013) Fibronectin and vitronectin promote human fetal osteoblast cell attachment and proliferation on nanoporous titanium surfaces. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9(6):1092–1097
Rotoli BM, Bussolati O, Costa AL, Blosi M, Cristo DL, Zanello PP, Bianchi MG, Visigalli R, Bergamaschi E (2012) Comparative effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on human airway epithelial cells and macrophages. J Nanopart Res 14(9):1069. doi:10.1007/s 1051- 12-1069-0
Sang XZ, Zheng L, Sun QQ, Li N, Cui YL, Hu RP, Gao GD, Cheng Z, Cheng J, Gui SX, Liu HT, Zhang ZL, Hong FS (2012) The chronic spleen injury of mice following long-term exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 100(4):894–902
Sayes CM, Wahi R, Kurian PA, Liu Y, West JL, Ausman KD, Warheit DB, Colvin VL (2006) Correlating nanoscale titania structure with toxicity: a cytotoxicity and inflammatory response study with human dermal fibroblasts and human lung epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci 92:174–185
Shi Y, Wang F, He J, Yadav S, Wang H (2010) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles cause apoptosis in BEAS-2B cells through the caspase 8/t-Bid-independent mitochondrial pathway. Toxicol Lett 2010(196):21–27
Shukla RK, Sharma V, Pandey AK, Singh S, Sultana S, Dhawan A (2011) ROS mediated genotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25:231–241
Shukla RK, Kumar A, Gurbani D, Pandey AK, Singh S, Dhawan A (2013) TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in human liver cells. Nanotoxicology 7(1):48–60. doi:10.3109/17435390.2011.629747
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantification of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175(1):184–191
Singh S, Shi TM, Duffin R, Albrecht C, Van Berlo D, Hoehr D, Fubini B, Martra G, Fenoglio I, Borm PJA, Schins RPF (2007) Endocytosis, oxidative stress and IL-8 expression in human lung epithelial cells upon treatment with fine and ultrafine TiO2: role of the specific surface area and of surface methylation of the particle. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222(2):141–151. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.05.001
Stringer B, Kobzik L (1998) Environmental particulate-mediated cytokine production in lung epithelial cells (A549): role of preexisting inflammation and oxidant stress. J Toxicol Environ Health a 55(1):31–44
Tang Y, Wang FD, Jin C, Liang H, Zhong X, Yang YJ (2013) Mitochondrial injury induced by nanosized titanium dioxide in A549 cells and rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(1):66–72. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.03.006
Tedja R, Marquis C, Lim M, Amal R (2011) Biological impacts of TiO2 on human lung cell lines A549 and H1299: particle size distribution effects. J Nanopart Res 13(9):3801–3813. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0302-6
Trouiller B, Reliene R, Westbrook A, Solaimani P, Schiestl RH (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce DNA damage and genetic instability in vivo in mice. Cancer Res 69(22):8784–8789. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
Turkez H (2011) The role of ascorbic acid on titanium dioxide-induced genetic damage assessed by the comet assay and cytogenetic tests. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63(5):453–457
Unfried K, Albrecht C, Klotz L-O, Von Mikecz A, Grether-Beck S, Schins R (2007) Cellular responses to nanoparticles: target structures and mechanisms. Nanotoxicology 1:52–71
Vamanu CI, Cimpan MR, Hol PJ, Sornes S, Lie SA, Gjerdet NR (2008) Induction of cell death by TiO2 nanoparticles: studies on a human monoblastoid cell line. Toxicol in Vitro 22:1689–1696. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2008.07.002
Wang JJ, Sanderson BJS, Wang H (2007a) Cyto- and genotoxicity of ultrafine TiO2 particles in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res 628(2):99–106
Wang JX, Zhou GQ, Chen CY, Yu HW, Wang TC, Ma YM, Jia G, Gao YX, Li B, Sun J, Li YF, Jia F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2007b) Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett 168(2):176–185
Warheit DB, Webb TR, Sayes CM, Colvin VL, Reed KL (2006) Pulmonary instillation studies with nanoscale TiO2 rods and dots in rats: toxicity is not dependent upon particle size and surface area. Toxicol Sci 91:227–236
Watanabe M, Okada M, Kudo Y, Tonori Y, Niitsuya M, Sato T, Aizawa Y, Kotani M (2002) Differences in the effects of fibrous and particulate titanium dioxide on alveolar macrophages of Fischer 344 rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 65:1047–1060
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Semp J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR, Nel AE (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano ett 6:1794–807
Yakovlev AG, Knoblach SM, Fan L, Fox GB, Goodnight R, Faden AI (1997) Activation of CPP32-like caspases contributes to neuronal apoptosis and neurological dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 17(19):74l5–7424
Yeo MK, Kang M (2012) The biological toxicities of two crystalline phases and differential sizes of TiO2 nanoparticles during zebrafish embryogenesis development. Mol Cell Toxicol 8:317–326. doi:10.1007/s13273-012-0039-z
Zhao F, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Chang XL, Chen CY, Zhao YL (2011) Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small 7:1322–1337
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31101357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Cui, H., Zhou, J. et al. Cytotoxicity, DNA damage, and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 5519–5530 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3717-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3717-7